Sleep apnea, a condition that disrupts the slumber of countless individuals, often lurks in the shadows of our bedrooms, unseen but deeply felt.
It’s a common challenge, yet many don’t realize that their evening libations could also be a silent contributor to restless nights.
In this article, we’ll delve into the complex relationship between alcohol consumption and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a prevalent sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep.

Our goal is to shed light on how even a modest nightcap can significantly impact those with OSA, potentially leading to more than just a groggy morning.
Understanding this connection is crucial whether you’re someone who enjoys a casual drink or living with sleep apnea. It’s about identifying the problem and empowering you with knowledge and practical advice to enhance your sleep quality and overall well-being.
So, let’s raise a glass to clarity and comfort as we navigate through the effects of alcohol on sleep apnea, backed by scientific insights and expert guidance.
By the end of this read, you’ll be equipped with the information you need to make informed decisions for restful nights and vibrant mornings.
The Impact of Alcohol on Sleep Apnea
When the lights go out, and the world quiets down, our bodies should naturally transition into a state of restful sleep.
However, for those living with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), this process is often disrupted.
OSA is a condition where an individual’s airway becomes partially or completely blocked during sleep, leading to pauses in breathing.
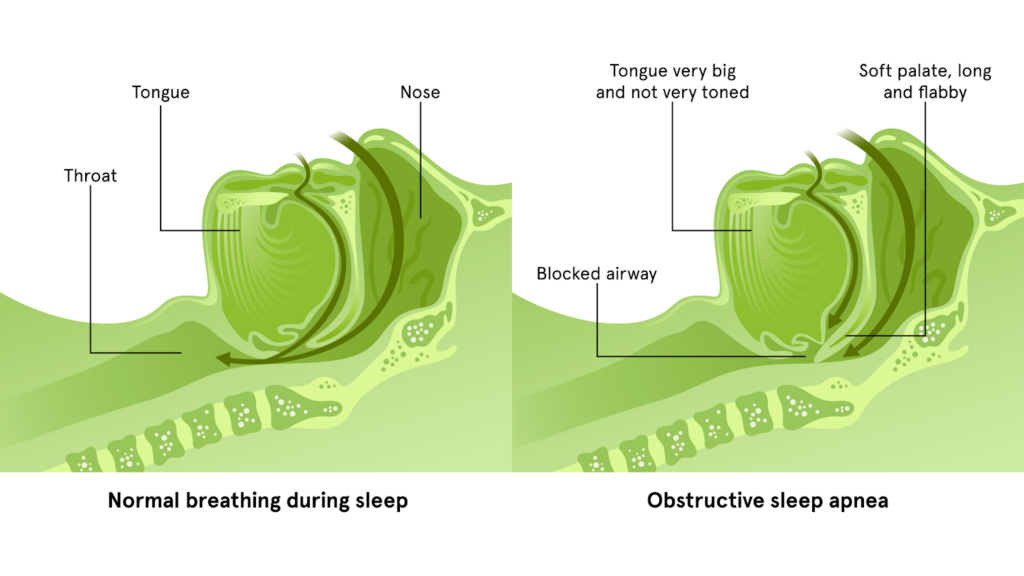
These interruptions can occur multiple times an hour, disrupting sleep quality and overall health.
Alcohol’s Effect on the Body and Sleep
Enter alcohol, a substance many turn to for its relaxing effects or as part of a social routine.
While a glass of wine or a pint of beer might seem like a ticket to unwind, for those with OSA, it’s a bit more complicated.
Alcohol is a central nervous system depressant, and when consumed, it can lead to excessive relaxation of the muscles in the body, including those in the throat.
This relaxation can exacerbate the airway obstruction that characterizes OSA.
The Sedative Impact on Sleep Mechanics
The sedative effect of alcohol also extends to the brain’s ability to respond to breathing difficulties during sleep.
Typically, if you stop breathing while asleep, the brain will trigger a wake-up response to reopen the airway.

However, alcohol can dampen this reflex, making it less likely for someone to wake up and breathe properly. This dampening leads to:
- Increased frequency and duration of breathing disruptions, known as apneas
- A decrease in the overall quality of sleep
Broader Implications for Sleep Health
Moreover, alcohol’s impact on sleep is not limited to those with diagnosed OSA.
It can also contribute to the development of sleep apnea in individuals who have not previously exhibited symptoms.
By altering the structure and function of the airway during sleep, alcohol can create an environment conducive to the onset of sleep apnea episodes.
Research Findings on Alcohol and Sleep Apnea
Investigations into the connection between alcohol and sleep apnea have yielded insights that are critical for those seeking to manage this sleep disorder effectively.
The research is robust, pointing to a clear relationship between alcohol consumption and the worsening of sleep apnea symptoms.
Understanding Alcohol’s Role in Sleep Disruption
Studies, such as the one published in Substance Abuse, have consistently demonstrated that alcohol has a direct impact on the severity of sleep apnea—with greater consumption leading to increased symptoms.
The sedative properties of alcohol can cause further relaxation of the throat muscles, which is particularly problematic for individuals with OSA.
This relaxation leads to an increased number of apneas, or pauses in breathing, and can extend the duration of these episodes throughout the night.
The Timing of Alcohol Consumption
According to The Sleep Foundation, The timing of alcohol intake plays a significant role in its effect on sleep quality.
Drinking alcohol close to bedtime can disrupt the natural sleep cycle and exacerbate the symptoms of sleep apnea.
The effects of alcohol on the body can persist for several hours, so even a drink with dinner can affect the quality of sleep later in the night.
Long-Term Implications for Health
The interaction between alcohol and sleep apnea can contribute to long-term health risks, as noted in this study published in the International Journal Of High Risk Behaviors And Addiction.
Reduced oxygen levels during sleep, a common consequence of both OSA and alcohol consumption, can lead to cardiovascular complications over time.
Additionally, the impact on sleep quality can affect cognitive function and mental health, making it a broader health concern.
Moderation and Management: Navigating Alcohol Consumption with Sleep Apnea
Living with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) requires an awareness of the various factors that can affect the condition, including the consumption of alcohol.
The research is clear: alcohol can have a significant impact on sleep quality for those with OSA.
However, understanding how to manage alcohol intake can play a pivotal role in mitigating its effects and maintaining good health.
The Importance of Moderation
The key to managing alcohol consumption when dealing with OSA is moderation.
By limiting the amount of alcohol consumed, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime, individuals can reduce the likelihood of exacerbating their sleep apnea symptoms.

It’s not just the amount of alcohol that matters, but also the timing of consumption.
Avoiding alcohol several hours before going to sleep can help prevent the alcohol-induced relaxation of throat muscles that contribute to airway obstruction.
Strategies for Responsible Drinking
For those with OSA who choose to drink, there are strategies that can help minimize the impact on sleep:
- Plan Ahead: If you plan to drink, do so earlier in the evening to give your body time to metabolize the alcohol before bedtime.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water alongside alcoholic beverages can help reduce alcohol’s dehydrating effects, which can worsen sleep quality.
- Choose Lower Alcohol Options: Opt for drinks with lower alcohol content to minimize the sedative effects on the body.
Obtaining Assistance from Healthcare Providers
It’s crucial for individuals with OSA to consult with their healthcare providers about their alcohol consumption.
A healthcare provider can offer personalized advice based on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health profile.

They can also provide guidance on how to use CPAP therapy effectively in conjunction with lifestyle changes.
Lifestyle Adjustments Beyond Alcohol
Managing OSA often requires a holistic approach to lifestyle changes. In addition to moderating alcohol intake, individuals can explore other adjustments such as:
- Improving Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants before bedtime can improve sleep quality.
- Weight Management: For some, weight loss can reduce the severity of OSA symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can improve sleep quality and overall health, which may reduce the symptoms of OSA.
CPAP Therapy: A Complementary Approach to Managing Sleep Apnea with Alcohol Consumption
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy is a cornerstone in managing obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
For those navigating the complexities of OSA with alcohol consumption, CPAP therapy can be an invaluable ally, offering a complementary approach to lifestyle changes for improved sleep quality.
Understanding CPAP Therapy
CPAP therapy involves a machine that delivers a steady stream of pressurized air through a mask, which keeps the airway open during sleep.
This treatment effectively reduces the number and severity of apneas for individuals with OSA.
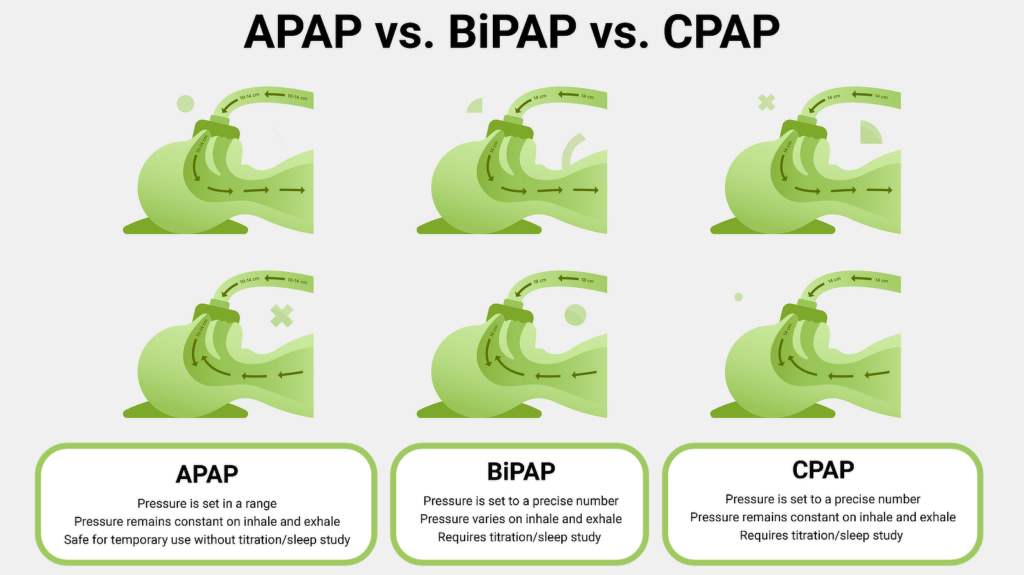
Different types of therapy and machines are available depending on what your primary care provider or sleep specialist feels would work best for your symptoms.
Check our comparison guide on APAP, BiPAP, and CPAP therapies for more information.
The Benefits of PAP Therapy in the Context of Alcohol Consumption
While lifestyle modifications, including reduced alcohol intake, are crucial, CPAP therapy provides additional support by:
- Maintaining Open Airways: Even if you continue to consume alcohol, PAP therapy can help prevent the collapse of the airway that leads to apneas.
- Improving Sleep Quality: By reducing apneas, PAP therapy helps ensure deeper, more restorative sleep, which is often disrupted by alcohol.
- Reducing Health Risks: Effective CPAP machine use can mitigate the cardiovascular risks associated with lowered oxygen levels during sleep caused by both OSA and alcohol.
Integrating CPAP with Lifestyle Changes
For those who consume alcohol, integrating CPAP therapy with lifestyle changes can enhance the management of OSA:
- Consistent Use: Ensuring consistent use of your CPAP equipment, even on nights when you consume alcohol, can help maintain the effectiveness of the therapy.
- Regular Monitoring: Keeping track of sleep patterns with and without alcohol consumption can help individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions about OSA management.
- Professional Guidance: Consulting with a sleep specialist can provide tailored advice on optimizing CPAP therapy in the context of alcohol consumption and individual health needs.
The Role of CPAP in Long-Term OSA Management
Long-term management of OSA often requires a multifaceted approach.
CPAP therapy is a central component of any effective long-term management plan, providing a direct intervention to maintain airway patency during sleep.
When combined with mindful alcohol consumption and other lifestyle adjustments, CPAP therapy can significantly improve the quality of life for those with OSA.
Frequently Asked Questions about Alcohol and Sleep Apnea
How exactly does alcohol affect my sleep apnea?
Alcohol relaxes the muscles in your throat, which can worsen obstructive sleep apnea by causing more frequent and prolonged breathing interruptions during sleep. Its sedative effects can also make it harder for your body to recover from apnea episodes, compounding symptoms of oxygen deprivation.
Can I still enjoy a drink if I have sleep apnea?
Yes, but moderation is key. It’s best to limit alcohol intake and avoid drinking several hours before bedtime to minimize its impact on your sleep. If you’re planning to drink later, choosing drinks with lower alcohol content can help to reduce the sedative effects as well.
Will using a CPAP machine allow me to drink alcohol without affecting my sleep apnea?
While CPAP therapy is effective in managing sleep apnea, alcohol can still affect the quality of your sleep. It’s advisable to moderate alcohol consumption even when using a CPAP machine.
Can alcohol consumption lead to the development of sleep apnea in someone without the condition?
Yes, heavy drinking can contribute to the onset of sleep apnea in individuals who did not previously exhibit symptoms by affecting the muscle tone in the throat and altering sleep patterns.
How long before bed should I stop drinking alcohol to ensure it doesn’t affect my sleep apnea?
Experts recommended to avoid alcohol at least 3-4 hours before bedtime. Doing so will give your body more time to metabolize the alcohol and reduce its impact on your sleep.
Are certain types of alcohol worse for sleep apnea than others?
The effects of alcohol on sleep apnea are more related to the quantity of alcohol consumed rather than the type. However, beverages with higher alcohol content may have a more significant impact.
If I wake up feeling fine, does that mean alcohol isn’t affecting my sleep apnea?
Not necessarily. You may not always be aware of the disruptions in your sleep caused by alcohol, as sleep apnea can prevent you from reaching the deeper, more restorative stages of sleep.
Can alcohol withdrawal affect sleep apnea?
Yes, withdrawal symptoms from alcohol can include sleep disturbances and may temporarily worsen sleep apnea. It’s essential to seek medical advice when reducing alcohol intake.
How can I tell if alcohol is affecting my CPAP therapy for sleep apnea?
Signs that alcohol may be impacting your CPAP therapy include:
- Feeling less rested upon waking
- Increased snoring
- Your CPAP machine is showing more frequent apneas
However, you should always consult your healthcare provider for the most accurate assessment.
Final Thoughts
The true value of rest lies not just in the absence of weariness but in the vibrant awakenings that greet you each morning and the energy to live life to its fullest.
It’s the tranquillity of mind that accompanies the knowledge that you’re nurturing your body, allowing it to restore and rejuvenate through the night.
Armed with the insights from this article, the power of transformation is in your hands.
It’s woven into the fabric of your daily choices, in your dedication to consistent CPAP therapy—even on those evenings graced by a toast—and in recognizing that while alcohol may offer a fleeting escape, enduring relaxation springs from a well of holistic health.

As you embark on this journey of nocturnal self-care, remember that managing sleep apnea is a commitment to your well-being.
It’s a pledge that calls for mindfulness and resolve, but the rewards—a day filled with energy and a life enriched with health—are immeasurably fulfilling.
Let this article be more than a mere compendium of facts; let it be the spark that ignites a transformation in your nightly ritual.
For in the quest for restorative sleep, every decision, every action, and every night is pivotal.
Should questions arise as you navigate the waters of CPAP therapy, know that CPAP Supply stands ready as Canada’s leading online provider in customer satisfaction.
Reach out to us for any inquiries about CPAP equipment and how to best harness PAP therapy in tandem with moderation to achieve your sleep goals.
Together with your healthcare team, we can chart a course to your best rest.
References:
Verywell Health: “What’s the Link Between Alcohol and Sleep Apnea?”
SleepApnea.org: “Alcohol and Sleep Apnea”
Sleep Care Online: “Does Alcohol Affect Sleep Apnea?”
Forbes Health: “How Does Alcohol Impact Sleep?”
American Addiction Centers: “Alcohol and Insomnia: How Alcohol Affects Sleep”
PubMed Central: “Disturbed Sleep and Its Relationship to Alcohol Use”
The Sleep Foundation: “Alcohol and Sleep Apnea”
WebMD: “Sleep Apnea”
International Journal of High Risk Behaviors and Addiction: “Associations of Alcohol Consumption and Chronic Diseases With Sleep Apnea Among US Adults”
Wiley Online Library: “Bedtime Ethanol Increases Resistance of Upper Airways and Produces Sleep Apneas in Asymptomatic Snorers”
PubMed Central: “Alcohol, snoring and sleep apnea.”
Irish Journal of Medical Science: “Alcohol as an independent risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea”
Sleep Medicine: “Alcohol and the risk of sleep apnoea: a systematic review and meta-analysis”
Handbook of Clinical Neurology: “Chapter 24 – Alcohol and the sleeping brain”

